
題目列表(包括答案和解析)
“In wilderness(荒野) is the preservation of the world.” This is a famous saying from a writer regarded as one of the fathers of environmentalism. The frequency with which it is borrowed mirrors a heated debate on environmental protection: whether to place wilderness at the heart of what is to be preserved.
As John Sauven of Greenpeace UK points out, there is a strong appeal in images of the wild, the untouched; more than anything else, they speak of the nature that many people value most dearly. The urge to leave the subject of such images untouched is strong, and the danger exploitation(開發(fā)) brings to such landscapes(景觀) is real. Some of these wildernesses also perform functions that humans need—the rainforests, for example, store carbon in vast quantities. To Mr. Sauven, these “ecosystem services” far outweigh the gains from exploitation.
Lee Lane, a visiting fellow at the Hudson Institute, takes the opposing view. He acknowledges that wildernesses do provide useful services, such as water conservation. But that is not, he argues, a reason to avoid all human presence, or indeed commercial and industrial exploitation. There are ever more people on the Earth, and they reasonably and rightfully want to have better lives, rather than merely struggle for survival. While the ways of using resources have improved, there is still a growing need for raw materials, and some wildernesses contain them in abundance. If they can be tapped without reducing the services those wildernesses provide, the argument goes, there is no further reason not to do so. Being untouched is not, in itself, a characteristic worth valuing above all others.
I look forward to seeing these views taken further, and to their being challenged by the other participants. One challenge that suggests itself to me is that both cases need to take on the question of spiritual value a little more directly. And there is a practical question as to whether wildernesses can be exploited without harm.
This is a topic that calls for not only free expression of feelings, but also the guidance of reason. What position wilderness should enjoy in the preservation of the world obviously deserves much more serious thinking.
1.John Sauven holds that________________.
A.many people value nature too much
B.exploitation of wildernesses is harmful
C.wildernesses provide humans with necessities
D.the urge to develop the ecosystem services is strong
2.What is the main idea of Para. 3?
A.The exploitation is necessary for the poor people.
B.Wildernesses cannot guarantee better use of raw materials.
C.Useful services of wildernesses are not the reason for no exploitation.
D.All the characteristics concerning the exploitation should be treated equally.
3.What is the author’s attitude towards this debate?
A.Objective. B.Disapproving. C.Sceptical. D.Optimistic.
4.Which of the following shows the structure of the passage?
A. B.
B.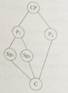 C.
C. D.
D.
CP: Central Point P: Point Sp: Sub-point(次要點(diǎn)) C: Conclusion
Wilderness
“In wilderness(荒野) is the preservation of the world.” This is a famous saying from a writer regarded as one of the fathers of environmentalism. The frequency with which it is borrowed mirrors a heated debate on environmental protection: whether to place wilderness at the heart of what is to be preserved.
As John Sauven of Greenpeace UK points out, there is a strong appeal in images of the wild, the untouched; more than anything else, they speak of the nature that many people value most dearly. The urge to leave the subject of such images untouched is strong, and the danger exploitation(開發(fā)) brings to such landscapes(景觀) is real. Some of these wildernesses also perform functions that humans need—the rainforests, for example, store carbon in vast quantities. To Mr.Sauven, these ”ecosystem services” far outweigh the gains from exploitation.
Lee Lane, a visiting fellow at the Hudson Institute, takes the opposing view. He acknowledges that wildernesses do provide useful services, such as water conservation. But that is not, he argues, a reason to avoid all human presence, or indeed commercial and industrial exploitation. There are ever more people on the Earth, and they reasonably and rightfully want to have better lives, rather than merely struggle for survival. While the ways of using resources have improved, there is still a growing need for raw materials, and some wildernesses contain them in abundance. If they can be tapped without reducing the services those wildernesses provide, the argument goes, there is no further reason not to do so. Being untouched is not, in itself, a characteristic worth valuing above all others.
I look forwards to seeing these views taken further, and to their being challenged by the other participants. One challenge that suggests itself to me is that both cases need to take on the question of spiritual value a little more directly. And there is a practical question as to whether wildernesses can be exploited without harm.
This is a topic that calls for not only free expression of feelings, but also the guidance of reason. What position wilderness should enjoy in the preservation of the world obviously deserves much more serious thinking.
【小題1】John Sauven holds that_____.
| A.many people value nature too much |
| B.exploitation of wildernesses is harmful |
| C.wildernesses provide humans with necessities |
| D.the urge to develop the ecosystem services is strong |
| A.The exploitation is necessary for the poor people. |
| B.Wildernesses cannot guarantee better use of raw materials. |
| C.Useful services of wildernesses are not the reason for no exploitation. |
| D.All the characteristics concerning the exploitation should be treated equally. |
| A.Objective. | B.Disapproving. | C.Sceptical. | D.Optimistic. |
A. | B. | C. | D. |
“In wilderness(荒野) is the preservation of the world.” This is a famous saying from a writer regarded as one of the fathers of environmentalism. The frequency with which it is borrowed mirrors a heated debate on environmental protection: whether to place wilderness at the heart of what is to be preserved.
As John Sauven of Greenpeace UK points out, there is a strong appeal in images of the wild, the untouched; more than anything else, they speak of the nature that many people value most dearly. The urge to leave the subject of such images untouched is strong, and the danger exploitation(開發(fā)) brings to such landscapes(景觀) is real. Some of these wildernesses also perform functions that humans need—the rainforests, for example, store carbon in vast quantities. To Mr. Sauven, these “ecosystem services” far outweigh the gains from exploitation.
Lee Lane, a visiting fellow at the Hudson Institute, takes the opposing view. He acknowledges that wildernesses do provide useful services, such as water conservation. But that is not, he argues, a reason to avoid all human presence, or indeed commercial and industrial exploitation. There are ever more people on the Earth, and they reasonably and rightfully want to have better lives, rather than merely struggle for survival. While the ways of using resources have improved, there is still a growing need for raw materials, and some wildernesses contain them in abundance. If they can be tapped without reducing the services those wildernesses provide, the argument goes, there is no further reason not to do so. Being untouched is not, in itself, a characteristic worth valuing above all others.
I look forward to seeing these views taken further, and to their being challenged by the other participants. One challenge that suggests itself to me is that both cases need to take on the question of spiritual value a little more directly. And there is a practical question as to whether wildernesses can be exploited without harm.
This is a topic that calls for not only free expression of feelings, but also the guidance of reason. What position wilderness should enjoy in the preservation of the world obviously deserves much more serious thinking.
【小題1】John Sauven holds that________________.
| A.many people value nature too much |
| B.exploitation of wildernesses is harmful |
| C.wildernesses provide humans with necessities |
| D.the urge to develop the ecosystem services is strong |
| A.The exploitation is necessary for the poor people. |
| B.Wildernesses cannot guarantee better use of raw materials. |
| C.Useful services of wildernesses are not the reason for no exploitation. |
| D.All the characteristics concerning the exploitation should be treated equally. |
| A.Objective. | B.Disapproving. | C.Sceptical. | D.Optimistic. |
A. | B. | C. | D. |
Wilderness
“In wilderness(荒野) is the preservation of the world.” This is a famous saying from a writer regarded as one of the fathers of environmentalism. The frequency with which it is borrowed mirrors a heated debate on environmental protection: whether to place wilderness at the heart of what is to be preserved.
As John Sauven of Greenpeace UK points out, there is a strong appeal in images of the wild, the untouched; more than anything else, they speak of the nature that many people value most dearly. The urge to leave the subject of such images untouched is strong, and the danger exploitation(開發(fā)) brings to such landscapes(景觀) is real. Some of these wildernesses also perform functions that humans need—the rainforests, for example, store carbon in vast quantities. To Mr.Sauven, these ”ecosystem services” far outweigh the gains from exploitation.
Lee Lane, a visiting fellow at the Hudson Institute, takes the opposing view. He acknowledges that wildernesses do provide useful services, such as water conservation. But that is not, he argues, a reason to avoid all human presence, or indeed commercial and industrial exploitation. There are ever more people on the Earth, and they reasonably and rightfully want to have better lives, rather than merely struggle for survival. While the ways of using resources have improved, there is still a growing need for raw materials, and some wildernesses contain them in abundance. If they can be tapped without reducing the services those wildernesses provide, the argument goes, there is no further reason not to do so. Being untouched is not, in itself, a characteristic worth valuing above all others.
I look forwards to seeing these views taken further, and to their being challenged by the other participants. One challenge that suggests itself to me is that both cases need to take on the question of spiritual value a little more directly. And there is a practical question as to whether wildernesses can be exploited without harm.
This is a topic that calls for not only free expression of feelings, but also the guidance of reason. What position wilderness should enjoy in the preservation of the world obviously deserves much more serious thinking.
【小題1】John Sauven holds that_____.
| A.many people value nature too much |
| B.exploitation of wildernesses is harmful |
| C.wildernesses provide humans with necessities |
| D.the urge to develop the ecosystem services is strong |
| A.The exploitation is necessary for the poor people. |
| B.Wildernesses cannot guarantee better use of raw materials. |
| C.Useful services of wildernesses are not the reason for no exploitation. |
| D.All the characteristics concerning the exploitation should be treated equally. |
| A.Objective. | B.Disapproving. |
| C.Sceptical. | D.Optimistic. |
A. | B. |
C. | D. |
“In wilderness(荒野) is the preservation of the world.” This is a famous saying from a writer regarded as one of the fathers of environmentalism. The frequency with which it is borrowed mirrors a heated debate on environmental protection: whether to place wilderness at the heart of what is to be preserved.
As John Sauven of Greenpeace UK points out, there is a strong appeal in images of the wild, the untouched; more than anything else, they speak of the nature that many people value most dearly. The urge to leave the subject of such images untouched is strong, and the danger exploitation(開發(fā)) brings to such landscapes(景觀) is real. Some of these wildernesses also perform functions that humans need—the rainforests, for example, store carbon in vast quantities. To Mr. Sauven, these “ecosystem services” far outweigh the gains from exploitation.
Lee Lane, a visiting fellow at the Hudson Institute, takes the opposing view. He acknowledges that wildernesses do provide useful services, such as water conservation. But that is not, he argues, a reason to avoid all human presence, or indeed commercial and industrial exploitation. There are ever more people on the Earth, and they reasonably and rightfully want to have better lives, rather than merely struggle for survival. While the ways of using resources have improved, there is still a growing need for raw materials, and some wildernesses contain them in abundance. If they can be tapped without reducing the services those wildernesses provide, the argument goes, there is no further reason not to do so. Being untouched is not, in itself, a characteristic worth valuing above all others.
I look forward to seeing these views taken further, and to their being challenged by the other participants. One challenge that suggests itself to me is that both cases need to take on the question of spiritual value a little more directly. And there is a practical question as to whether wildernesses can be exploited without harm.
This is a topic that calls for not only free expression of feelings, but also the guidance of reason. What position wilderness should enjoy in the preservation of the world obviously deserves much more serious thinking.
67. John Sauven holds that________________.
A. many people value nature too much
B. exploitation of wildernesses is harmful
C. wildernesses provide humans with necessities
D. the urge to develop the ecosystem services is strong
68. What is the main idea of Para. 3?
A. The exploitation is necessary for the poor people.
B. Wildernesses cannot guarantee better use of raw materials.
C. Useful services of wildernesses are not the reason for no exploitation.
D. All the characteristics concerning the exploitation should be treated equally.
69. What is the author’s attitude towards this debate?
A. Objective. B. Disapproving. C. Sceptical. D. Optimistic.
70. Which of the following shows the structure of the passage?
A.  B.
B.  C.
C.  D.
D. 
CP: Central Point P: Point Sp: Sub-point(次要點(diǎn)) C: Conclusion
湖北省互聯(lián)網(wǎng)違法和不良信息舉報平臺 | 網(wǎng)上有害信息舉報專區(qū) | 電信詐騙舉報專區(qū) | 涉歷史虛無主義有害信息舉報專區(qū) | 涉企侵權(quán)舉報專區(qū)
違法和不良信息舉報電話:027-86699610 舉報郵箱:58377363@163.com